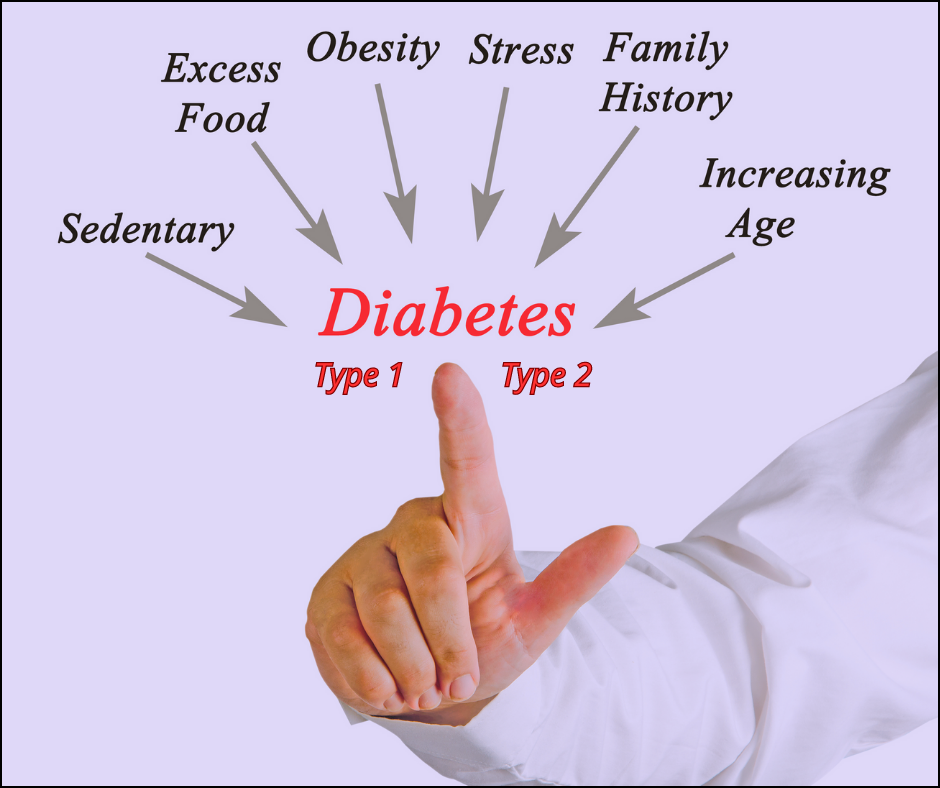
Type 1 & type 2 diabetes: The main difference between the type 1 & type 2 diabetes is that type 1 diabetes is a genetic condition that often shows up early in life & type 2 is mainly lifestyle-related & develops over time. With type 1 diabetes, your immune system is attacking & destroying the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas.
Type 1 diabetes:
Is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. People with type 1 diabetes need insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels. https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/about-diabetes/type-1-diabetes/
Symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Extreme hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Extreme fatigue
- Cuts & bruises that are slow to heal
- Feeling irritable or having other mood changes
- Weight loss & loss of muscle bulk
- Itchiness around the genital area, or regular bouts of thrush (a yeast infection)
- Sweet smell of urine
- Bed-wetting in children who have never wet the bed during the night
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, proper diet, exercise & insulin therapy.
Cause:
- Family history – Anyone with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes has a slightly higher risk of developing the condition
- Genetics – Having certain genes increases the risk of developing type 1 diabetes
- Geography – African Americans, Alaska Natives, American Indians, Asian Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, Native Hawaiians & Pacific Islanders seem to be at higher risk
- Age
- Overweight or obesity
- Some hormonal diseases cause the body to produce too much of certain hormones, which sometimes cause insulin resistance and diabetes – Cushing syndrome, acromegaly, hyperthyroidism & pancreatitis
Treatments:
- Eating a health & balanced diet
- Check blood sugar levels
- Exercise
- Keeping away from sugars in any form
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stay hydrated (Intake of about 8-10 glasses of water for a diabetic person)
- Sleep cycle (7-8 hours of sound sleep every day. Your sleep has direct effects on your blood sugar levels
- Insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage blood sugar levels

Type 2 diabetes:
Is a chronic condition in which the body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to use insulin. This leads to higher blood sugar levels over time. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factor like obesity & physical inactivity, although genetics may also play a role. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html
Symptoms:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Increased hunger
- Unintended weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck
- Sweet smell when urinating
Causes:
Type 2 diabetes is the result of two problems:
- Cells in muscle, fat & the liver become resistant to insulin as a result, the cells don’t take in enough sugar
- The pancreas can’t make enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range
- Plus being overweight & inactive are key contributing factors
Risk factors:
- Being overweight or obese is a main risk
- Fat distribution – Storing fat in the abdomen — rather than the hips and thighs — indicates a greater risk. The risk of type 2 diabetes is higher in men with a waist circumference above 40 inches (101.6 centimetres) and in women with a waist measurement above 35 inches (88.9 centimetres)
- The less active a person is, the greater the risk. Physical activity helps control weight, uses up glucose as energy & makes cells more sensitive to insulin
- Family history – An individual’s risk of type 2 diabetes increases if a parent or sibling has type 2 diabetes
- Race and ethnicity – Although it’s unclear why, people of certain races & ethnicities. This includes Hispanic, Native American, Asian people & Pacific Islanders are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than other races
- Blood lipid levels – An increased risk is evident with low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol — the “good” cholesterol — and high levels of triglycerides
- The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after age 35
- Prediabetes is a condition in which the blood sugar level is higher than normal, but not high enough to classify as diabetes. Left untreated it often progresses to type 2 diabetes
- Pregnancy-related risks – The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher in people who had gestational diabetes when they were pregnant and in those who gave birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds (4 kilograms)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome – Having polycystic ovary syndrome a condition characterised by irregular menstrual periods, excess hair growth & obesity increases the risk of diabetes
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes like eating a healthy diet that is low in carbohydrates & saturated fats
- Exercising
- Losing weight if necessary
- Eating foods rich in fibre and healthy carbohydrates — eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help keep your blood glucose levels steady
- Eating at regular intervals
- Learning to listen to your body and learn to stop eating when you’re full
- The use of medications & insulin therapy in some case
- Manage blood glucose levels
Summary:
Individuals with hypoglycaemia, hyperglycaemia, type 1 & type 2 diabetes should work with their healthcare team to develop an individualised treatment plan. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, as well as regular communication with a healthcare provider, can help ensure that blood sugar levels remain stable & reduce the risk of complications.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as following a balanced diet https://www.nutritionalhealthenterprises.com/health-benefits-of-a-mediterranean-diet/ & engaging in regular exercise, can have a significant impact on managing and preventing blood sugar imbalances.
Disclaimer:
All content & media on the Natural Therapy Clinic is created & published online for informational purposes only.